Beyond the Neck: Whiplash can cause Hearing Loss & Tinnitus
Unfortunately, whiplash injuries resulting from motor vehicle collisions can have a significant impact on both hearing loss and tinnitus. The complex and delicate structures of the neck and head are vulnerable to the sudden forces involved in whiplash, leading to various auditory disturbances. Hearing loss following whiplash injuries can result from several mechanisms, including direct trauma to the ear, damage to the auditory nerve, or disturbances in the inner ear's fluid balance.
The severity of hearing loss may vary, ranging from mild to profound, and can be temporary or permanent. Motor vehicle accidents are an unfortunate reality that affects millions of lives worldwide. Whiplash injuries, commonly associated with rear-end collisions, have long been recognized as a leading cause of neck and back pain. However, recent research has unveiled a less known, yet significant consequence of whiplash – its potential to trigger hearing loss and tinnitus. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate connection between whiplash injuries and auditory issues, shedding light on the silent consequences that victims may experience long after the initial accident.
Understanding Whiplash Injuries
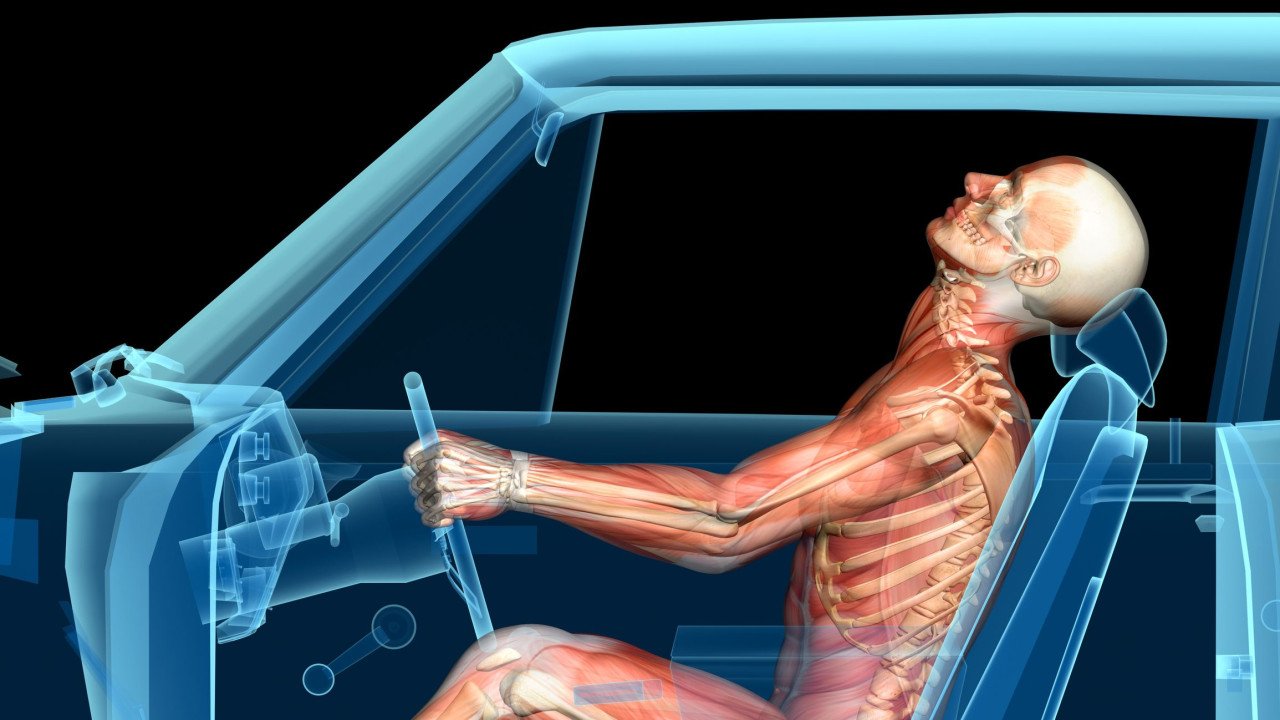
Whiplash is a term used to describe a range of neck injuries resulting from the rapid back-and-forth motion of the head, resembling the cracking of a whip. It commonly occurs in rear-end motor vehicle accidents, where the force of impact causes the neck to extend beyond its normal range of motion. This abrupt movement can lead to damage to soft tissues, ligaments, tendons, and muscles in the neck, as well as the cervical spine.
Whiplash and Its Impact on Hearing
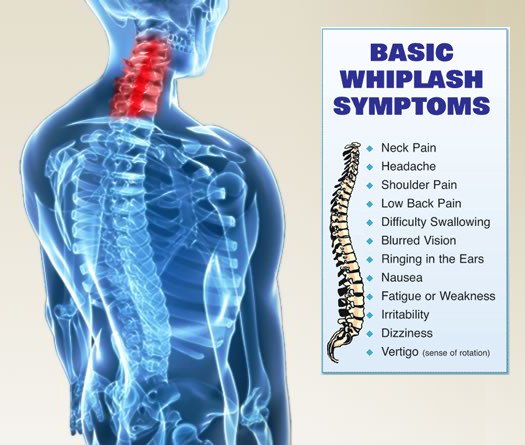
While the immediate symptoms of whiplash usually involve neck pain, stiffness, and headaches, the damage extends beyond these localized symptoms. Recent studies have shown a surprising correlation between whiplash injuries and hearing-related problems like hearing loss and tinnitus.
- Inner Ear Damage
The inner ear plays a crucial role in converting sound vibrations into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain for interpretation. In a whiplash injury, the sudden and forceful movement of the head can cause a shear force within the inner ear structures, potentially leading to microscopic tears in delicate tissues. These tears can disrupt the normal function of the inner ear and result in sensorineural hearing loss.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction
Whiplash injuries can also lead to dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, which connects the jawbone to the skull. TMJ dysfunction can cause referred pain in the ear area and disturb the proper functioning of the middle ear. Consequently, individuals may experience changes in hearing sensitivity and tinnitus.
- Neurological Damage
Whiplash injuries can cause trauma to the neck and head, leading to neurological damage that affects the auditory pathways. This disruption can cause miscommunication between the brain and the auditory system, resulting in hearing issues such as reduced auditory processing speed, difficulty understanding speech, and increased sensitivity to sound (hyperacusis).
The Tinnitus Connection
Tinnitus, often described as a ringing or buzzing sensation in the ears, is a common symptom that can arise after whiplash injuries. Although the exact mechanisms linking whiplash to tinnitus are not yet fully understood, several theories offer insights into this perplexing connection:
Cochlear Damage: As mentioned earlier, inner ear damage caused by whiplash can lead to abnormal electrical signals being sent to the brain. These distorted signals may manifest as tinnitus sounds.
Somatosensory Tinnitus: Whiplash injuries can affect the neck's sensory nerves, creating a condition known as somatosensory tinnitus. In this case, movements of the neck and head can trigger or modulate the tinnitus perception.
Central Nervous System Involvement: Whiplash can cause changes in brain activity and connectivity, influencing the brain's auditory processing centers. This alteration in neural activity might contribute to the development or intensification of tinnitus.
The Long-term Impact on Quality of Life
Hearing loss and tinnitus resulting from whiplash injuries can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, leading to emotional distress, social isolation, and reduced overall well-being. As these auditory issues often emerge long after the accident, victims might not immediately connect them to the past injury, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If you or someone you know experiences hearing difficulties or tinnitus following a whiplash injury, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial. A comprehensive evaluation by an audiologist and a medical professional can help determine the extent of the auditory damage and rule out other potential causes.
Treatment options for hearing loss and tinnitus related to whiplash injuries may include:
- Hearing Aids: Sensorineural hearing loss can often be managed with hearing aids, which amplify sound and improve communication abilities.
- Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT): TRT is a therapeutic approach that aims to habituate the brain to perceive tinnitus as a neutral sound, reducing its emotional impact.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can be beneficial for managing the emotional distress and anxiety associated with hearing loss and tinnitus.
- Physical Therapy: For TMJ dysfunction resulting from whiplash, physical therapy and exercises may help alleviate symptoms and improve jaw function.
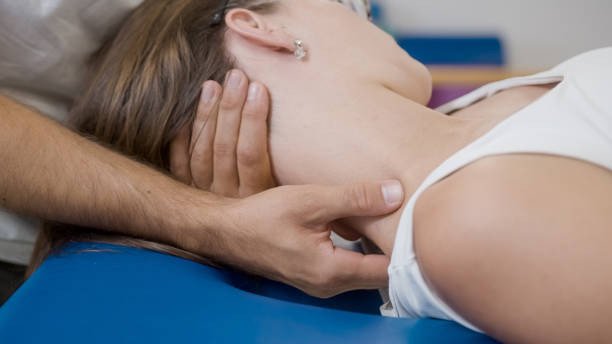
Chiropractic Care and Adjusting the Cervicals
Chiropractic care, a non-invasive and holistic approach to healthcare, has shown promising potential in addressing tinnitus and hearing loss. Although primarily associated with spinal adjustments to alleviate musculoskeletal issues, chiropractic techniques aim to optimize nervous system function, which includes the auditory pathways. Studies suggest that misalignments in the cervical spine can interfere with nerve signals traveling to and from the ears, potentially contributing to tinnitus and hearing problems. Chiropractors, through gentle adjustments, seek to realign the vertebrae, reduce nerve impingements, and promote better nerve communication, which may result in improved auditory function.
Additionally, chiropractic care's focus on overall health and wellness may lead to benefits beyond spinal alignment, such as reducing inflammation and enhancing blood flow to the ears, thus creating a conducive environment for healing. While further research is warranted to establish the full extent of chiropractic's efficacy in treating and curing tinnitus and hearing loss, its non-invasive nature and potential positive impact on nerve function offer a promising avenue for those seeking alternative and complementary approaches to traditional audiological treatments.
Traditional Chinese Medicine
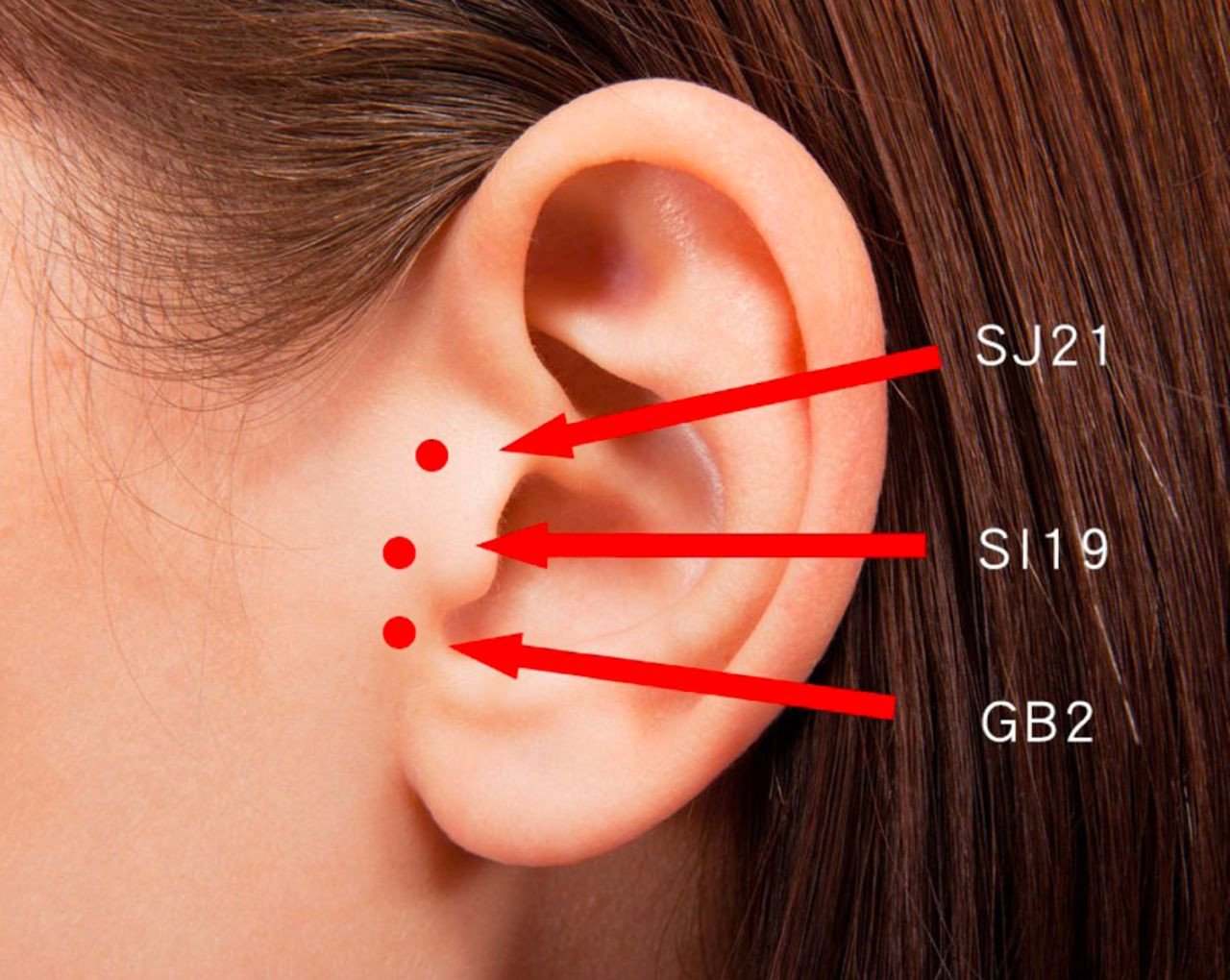
From a different perspective, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) considers tinnitus and hearing loss to be a result from imbalances in the body's vital energy, or "qi." TCM practitioners identify specific patterns of disharmony that contribute to tinnitus, and treatment aims to restore balance and harmony within the body. Herbal supplements, often prescribed as personalized formulas based on an individual's unique symptoms and constitution, are used to nourish deficiencies, disperse stagnation, and calm the mind.
Commonly used herbs may include Ginkgo biloba, Ligustrum lucidum, and Paeonia suffruticosa. Additionally, acupuncture, the practice of inserting thin needles into specific points on the body, is employed to regulate the flow of qi and blood, addressing the underlying imbalances. By combining these therapeutic modalities, TCM seeks to alleviate tinnitus symptoms, improve overall well-being, and target the root cause of the condition, providing a comprehensive and integrative approach to tinnitus management. As with any medical treatment, individuals considering TCM for tinnitus should consult qualified practitioners to ensure safe and effective care.
Final Thoughts
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to improving the prognosis and preventing further hearing deterioration. Furthermore, tinnitus can emerge as a common symptom following whiplash injuries. The link between the two lies in the intricate network of nerves and blood vessels in the head and neck region. Whiplash-induced damage or inflammation in this area can disrupt the normal functioning of the auditory system, leading to the perception of phantom sounds, such as ringing, buzzing, or hissing. Traditional treatments, such as medication and physical therapy, may be beneficial in managing the symptoms. Additionally, integrating complementary approaches, like acupuncture or chiropractic care, may aid in alleviating discomfort and promoting overall well-being.
Moreover, preventive measures play a vital role in reducing the risk of whiplash injuries and their associated auditory consequences. Using seat belts, maintaining proper headrest positioning, and driving attentively can all contribute to minimizing the impact of motor vehicle collisions on the neck and head region.
In conclusion, individuals who experience hearing loss or tinnitus following a whiplash injury should take their symptoms seriously and seek immediate medical attention. Timely intervention and comprehensive management strategies, including conventional and complementary approaches, can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Additionally, promoting road safety and adopting preventive measures are essential steps in reducing the incidence and severity of whiplash injuries and their auditory implications. By raising awareness of the potential link between whiplash and hearing-related issues, we can foster a safer environment on the roads and enhance the overall well-being of individuals impacted by these conditions.
Sources
- Claussen C, Constantinescu L. Tinnitus in Whiplash Injury. Int Tinnitus J. 1995;1(2):105-114. PMID: 10753331.
- Lee SJ, Bae CH, Seo JP, Jang SH. Diagnosis of Tinnitus Due to Auditory Radiation Injury Following Whiplash Injury: A Case Study. Diagnostics (Basel). 2019 Dec 30;10(1):19. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10010019. PMID: 31905965; PMCID: PMC7168912.
- Fitzgerald DC. Head trauma: hearing loss and dizziness. J Trauma. 1996 Mar;40(3):488-96. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199603000-00034. PMID: 8601878.
- Bhatt YM, de Carpentier JP. Musical hallucination following whiplash injury: case report and literature review. J Laryngol Otol. 2012 Jun;126(6):615-8. doi: 10.1017/S0022215112000242. PMID: 22643207.
- Yin Yang House | Study Finds Acupuncture Effective for Chronic Tinnitus
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.